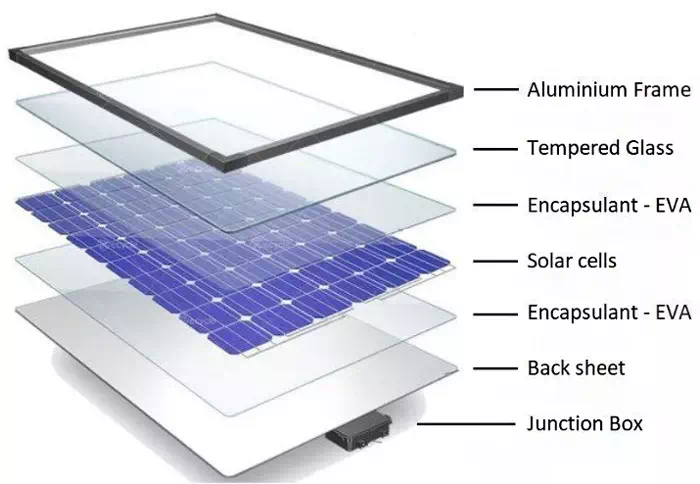
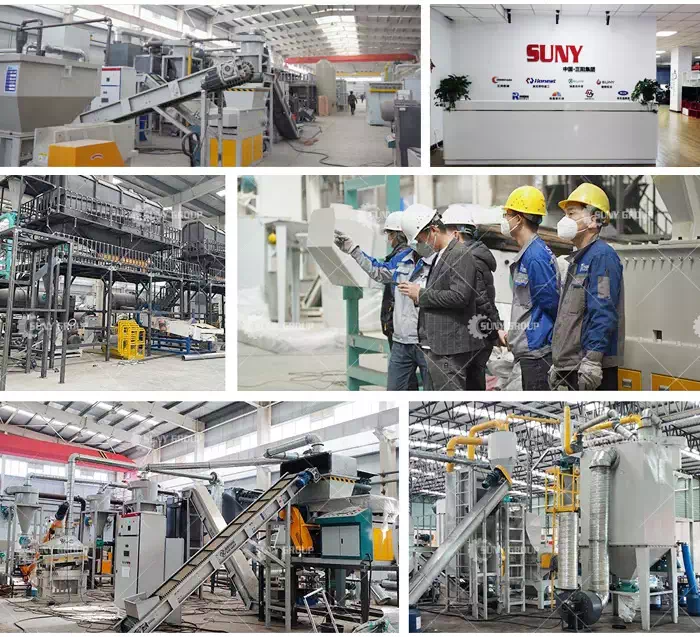
RECYCLING TECHNOLOGY
Photovoltaic panels contain high components such as glass, aluminum, adhesive sealant, silicon, and silver, as well as rare metals such as steel and gallium, which have very good resource utilization value. SUNYGROUP's equipment recycles waste photovoltaic panels through physical means such as automatic dismantling, crushing, and sorting, so as to achieve the purpose of recycling useful components.
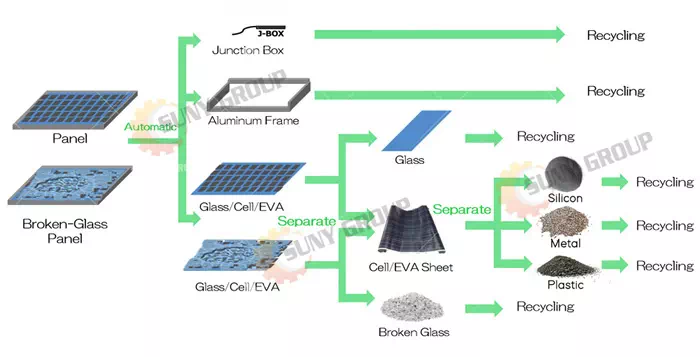
① The power box and aluminum frame of the solar panel are removed by a specialized dismantling machine.

② Remove glass on the photovoltaic panel by a glass remover machine.This is the photovoltaic panel after removing the glass:

③ The solar photovoltaic panels with the aluminium frame and glass removed enter the twin shaft shredder. The twin-shaft shredder tears the PV panels into strips. Next, the material enters the crusher. The shredder crushes the material into small pieces of 1-2 cm.

④ Through negative pressure feeding, these small pieces will enter the Fine grinder.The fine grinder we configure is with return material, if the particle size is unqualified, it will be returned to the fine grinder.Qualified sizes enter the air separator.The metal powder is screened out from one side of the air separatorThe other side is plastic and a small amount of metal.
⑤ These plastics and a small amount of metal enter the electrostatic separator.The pure plastic and metal are again sorted out.This is part of the output of solar photovoltaic panels after crushing, sorting and recycling:

EQUIPMENT STRUCTURE
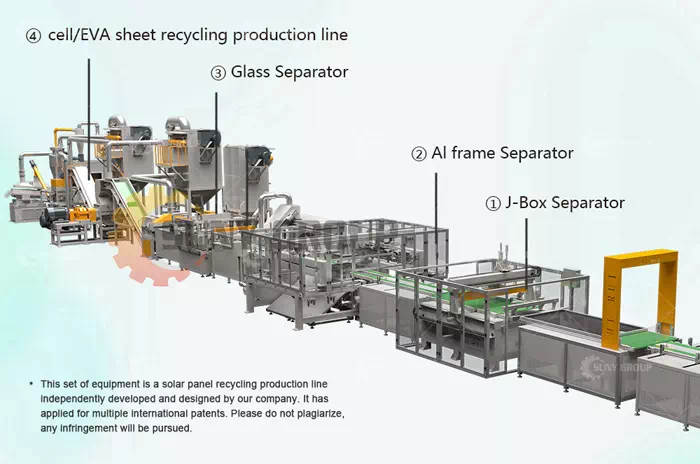
PART 1: J-Box Separator;
PART 2: Al frame Separator;
PART 3: Glass Separator;
PART 4: cell/EVA sheet recycling production line.
MAIN MACHINES




J-boxre moving machine: Suitable for solar panels with one or more J-boxes.
Glass removing machine: Removing most of the glass from the surface Processing Width 1250mm.
Aluminum frame removing machine: Removing the aluminum frame at the edge of the solar panel.
Crushing and sorting machines: The treated solar panels then pass through the crushing and sorting equipment to obtain metal powder.
TECHNICAL PARAMETER
ModelPowerSize(mm)Capacity
ZYSP-1500260kw44000*8000*500040-80pcs/h
SALES AREA:

ادامه مطلب

Furnace Draining
Before repairing a furnace, the glass needs to be drained from the tank. HORN® provides special equipment and experienced people to drain the glass in a safe and effective way.
READ MORE

Tin Bath Shutdown
If the tin bath requires a cold repair or needs to be preserved before a period of non-use, it must first be taken out of operation. An uncontrolled shutdown can lead to the loss of the whole tin bath, which is why it is not recommended.
READ MORE

Hot Repairs
HORN® Bau & Service GmbH provides a full-service package during furnace operation to maintain the furnace and to secure a long furnace lifespan, e.g. by thermal regenerator cleaning and flux line paving.
READ MORE

Installation Works
At the construction site the unique working conditions such as extreme temperatures, call for a team of highly qualified specialists and experts. HORN® employs a pool of very experienced people who have been working in the glass industry for many years.
READ MORE

Supervision
The HORN® experts ensure the correct installation and commissioning of all plant components and lay the foundation for a successful production.
READ MORE

Heat Up
The controlled heat up process of the various production areas is essential for a smooth start. HORN® provides you with the equipment and the necessary knowledge.
READ MORE

Furnace Hot Inspection
With the HORN® inspection service the glass plant team can easily observe the inside of the furnace by endoscope and exactly determine necessary repair works or remaining lifespan.
READ MORE
Glass Melting Furnaces
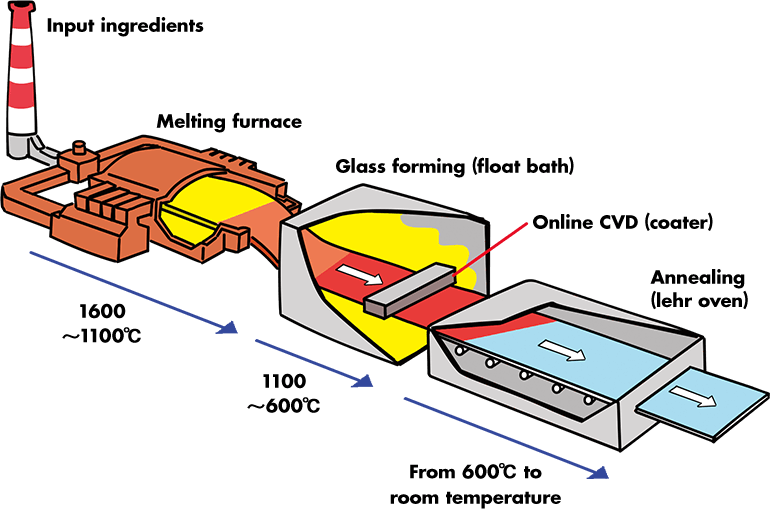
The type of furnace for melting glass typically depends on the type and quantity of glass being produced, and the local fuel and utility costs. While there are exceptions, the following discussion describes the primary furnace types and the glass segments that most commonly use each style.
There are two types of glass melting furnaces: Pot furnaces and Tank furnaces.
Pot Furnaces are structures built of refractory materials in which there is no contact between the furnace and the glass. Glass is melted in several pots made of refractory materials which are resistant to glass attack at high temperatures. The pots are charged with a batch, which is melted over a number of hours and worked on a 24 or 18 hour cycle. An average pot can hold 600-700 kg of glass. Pot furnaces are used where the glass is formed by hand and mouth blowing. One of the main advantages of this system is that several types of glasses can be melted at the same time. A pot can be used for about 30 melting cycles and thus produce between 18 and 21 tonnes of glass.
Fuel economy is normally achieved by recuperation, i.e., the pre-heating of combustion air by waste heat from the furnace exhaust gases. In this system the pre-heating of the combustion air is done by passing the air through metal tubes on the outside of which the exhaust gases flow towards the chimney. Thus the heat exchange is continuous. Electricity can also be used for melting.
Tank furnaces
Tank Furnaces are used where continuous flow of glass is needed to feed automatic glass forming machines. They are more economical in their use of fuel and are used mainly for the large scale production of containers, flat glass, electric bulbs, tubing and domestic machine made tableware. A large float glass furnace can have a capacity of 2,000 tonnes.
A tank furnace consists of a bath, built of a very special high refractory material, which can resist chemical attack of molten glass at temperatures in excess of 1500°C and a superstructure where combustion takes place. The quality of refractory materials, used for building the bath, has improved to such an extent that whereas some 30 years ago, the life of a furnace was well below 2 years, it is now over 9 years.
In order to achieve high melting temperatures and fuel economy, a regenerative or recuperative system is used. Both these systems utilise the waste heat of combustion for pre-heating the incoming combustion air.
While in the recuperative system the heat exchange between the combustion air and waste gases is continuous, in the regenerative system the waste gases are passed through a large chamber packed with refractory bricks arranged in a pattern which permits free flow of the gases. The brickwork is heated by the waste gases and after having been heated for some minutes, the direction of firing is reversed. Combustion air is passed through the chamber and the heat thus collected in the brickwork is used for pre-heating the combustion air. The firing is thus from right to left, during which time the right hand generator is heated and so there is a reversal of firing every x minutes. The cycle time can be changed for best heat exchange results and modern furnaces have computer managed control systems, which adjust the time of firing in each direction to achieve the best heat exchange conditions.
Heavy fuel oil or natural gas is normally used for firing tank furnaces. Glass, being an electrical conductor at high temperature, can also be melted by electricity. However, electricity is far too expensive and is normally used to boost the output from a gas or oil fired furnace. Nevertheless, technological progress in electric melting has enabled the use of all electric glass melting furnaces even at the high cost of electricity.
Unit melter
The term unit melter is generally given to any fuel-fired glass-melting furnace that has no heat recovery device. Generally, one is referring to an air/fuel-fired furnace when using this furnace term. However, most full oxy/fuel furnaces have no heat recovery system and are therefore, technically unit melters. Typically, the air/fuel unit melters are relatively small in size and are fired with 2 to 16 burners. Furnaces range in production from as large as 36 t of glass per day to as small as 230 kg of glass per day. Larger air/fuel unit melters are found in areas where fuel is extremely cheap. Frit, tableware, opthamalic glass, fiberglass, and specialty glasses with highly volatile and corrosive components are produced in unit melters. Due to the very low energy efficiency and the use of individual burners, the air/fuel unit melters are very amenable to oxygen-enhanced combustion techniques, including supplemental oxy/fuel boosting, premixed oxygen enrichment, and full oxy/fuel combustion. Oxy/fuel unit melters have been built as large as 320 t per day of glass to as small as 230 kg of glass per day.
Recuperative melter
A recuperative melter is a unit melter equipped with a recuperator. Typically, the recuperator is a metallic shell-and-tube-style heat exchanger that preheats the combustion air to 540 to 760°C. The furnace is fired with 4 to 20 individual burners. These furnaces range in size from as large as 250 t per day of glass to as small as 18 t per day of glass. These furnaces are common in fiberglass production but can also be used to produce frit. Some recuperative furnaces are used in the container industry, though this is not common. Furnace life is a function of glass type being produced. For example, a 6-year furnace life is typical for wool fiberglass. A typical recuperative melter is shown in the following figure.
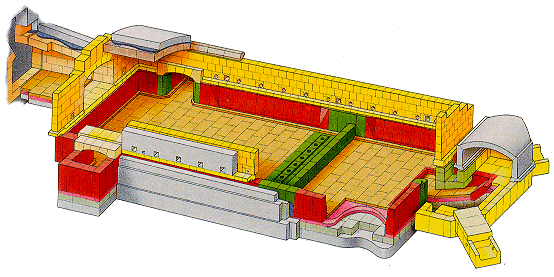
Chart 1: Typical recuperative melter (side view)
The recuperative melter is amenable to supplemental oxy/fuel technique or the premixed oxygen enrichment technique. Oxygen lancing is typically not used. In the supplemental oxy/fuel technique, an air/fuel burner is simply replaced by an oxy/fuel burner. When premix is applied, oxygen injection into the air main typically occurs downstream of the recuperator to avoid problems associated with air leaks in the recuperator. Care should be taken in locating the oxygen diffuser.
These furnaces are good candidates for full oxy/fuel. Recuperative heat exchanger efficiencies are much lower than with regenerative furnaces, and therefore fuel savings can help to drive the conversion. Also, recuperative furnaces operate in a continuous and steady firing mode of operation similar to oxy/fuel furnaces.
All-electric melter
As the name implies, all-electric melters receive all of the energy for glass melting through electrical heating. Electric current is passed through the glass by means of electrodes. Because of the electrical resistance of the glass, the glass is heated by Joulean heating. Electrodes are typically made of molybdenum; however, tin oxide, platinum, graphite, and iron have also been used. The electrodes are usually rod-or plate-type and can be located in the melter side walls or bottom.
The refractory tends to degrade much faster in these furnaces, resulting in very short furnace campaigns, typically less than 2 years. Most of these furnaces are less than 36 t of glass per day; however, furnaces as large as 180 t per day have been built. A typical electric melter is shown in figure below.
Due to the design of these furnaces, there is typically no fit for oxygen-enriched combustion. One exception is “hot top” melters which provide some heat via burners located above the bath. In this latter case, supplemental oxy/fuel or premixed oxygen enrichment has been practiced.
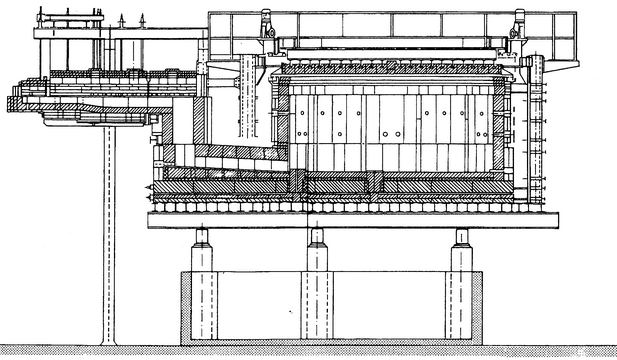
Chart 2: Typical electric melter
Regenerative or Siemens furnace
The regenerative furnace was patented in the U.S. by Siemens Corporation in the late 19th century. While some design evolution has occurred, the basic concept has remained unchanged. In a regenerative furnace, air for combustion is preheated by being passed over hot regenerator bricks, typically called checkers. This heated air then enters an inlet port to the furnace. By using one or more burners, fuel is injected at the port opening, mixes with the air, and burns over the surface of the glass. Products of combustion exhaust out of the furnace through a nonfiring port and pass through a second set of checkers, thereby heating them. After a period of 15 to 30 min, a reversing valve changes the flow and the combustion air is passed over the hot checkers that were previously on the exhaust side of the process. The fuel injection system also reverses. After reversing, the exhaust gases pass through and heat the checkers that had previously heated the combustion air.
The Siemens furnace is the workhorse of the glass industry. Most flat glass and container glass are produced in this furnace type. Regenerative furnaces are also used in the production of TV products, tableware, lighting products, and sodium silicates. There are two common variants of the Siemens furnace: the side-port regenerative melter, and the end-port regenerative melter.
End-Port Regenerative Furnace
End-port regenerative furnaces are typically used for producing less than 230 t of glass per day. In an end-port furnace, the ports are located on the furnace back wall. Batch is charged into the furnace near the back wall on one or both of the side walls. The following figure shows the layout of a typical end port furnace. These furnaces are commonly used for producing container glass, but are also used for producing tableware and sodium silicates. For container production, a furnace campaign typically lasts 8 years.
Undershot of oxygen through lances and supplemental oxy/fuel have been used successfully on this type of furnace. Oxygen enrichment of the preheated combustion air has also been used on furnaces with damaged checkers.
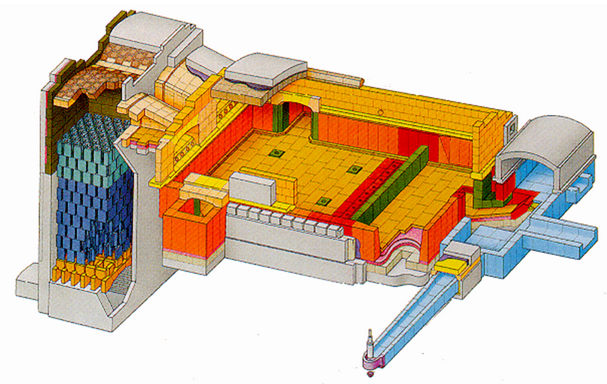
Chart 3: Typical end-port regenerative furnace
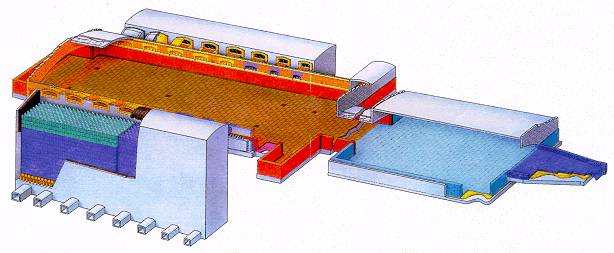
Side-Port Regenerative Furnace
Side-port regenerative furnaces have ports located on the furnace side walls. Batch is charged into the furnace from the back wall. The next figure shows the layout of a typical side-port furnace. Side-port regenerative furnaces are typically used for producing greater than 230 t of glass per day. A side-port furnace for float glass commonly produces 460 to 630 t of glass per day. For container glass, side-port furnaces ordinarily produce between 230 to 320 t of glass per day. These furnaces are commonly used in container and float glass production, but are also used for the production of tableware and sodium silicates. For container production, a furnace campaign typically lasts 8 years and for float glass production can last as long as 12 years.
Undershot and supplemental oxy/fuel oxygen enrichment have been successfully used on this type of furnace. Premix enrichment has also been used on furnaces with damaged checkers. These furnaces have also been converted to full oxy/fuel.
Solar Glass Factory

5mm Iow iron altra-clear solar float glas in AR coating process

AR Coating process

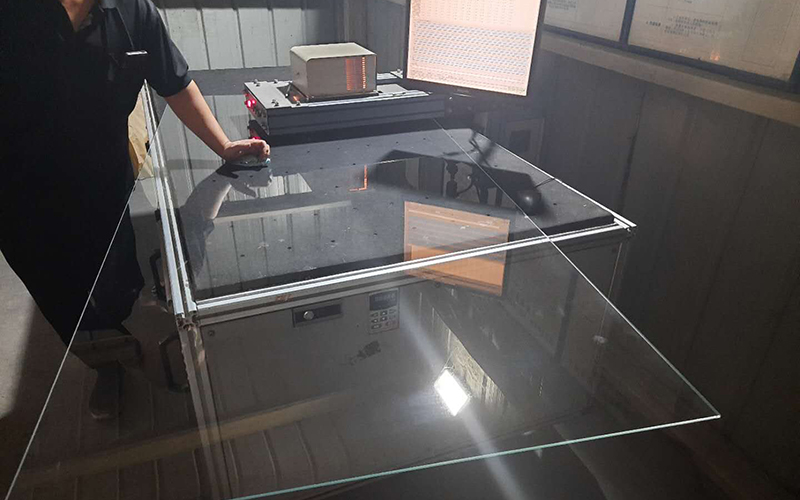
Inspection flatness of glasses
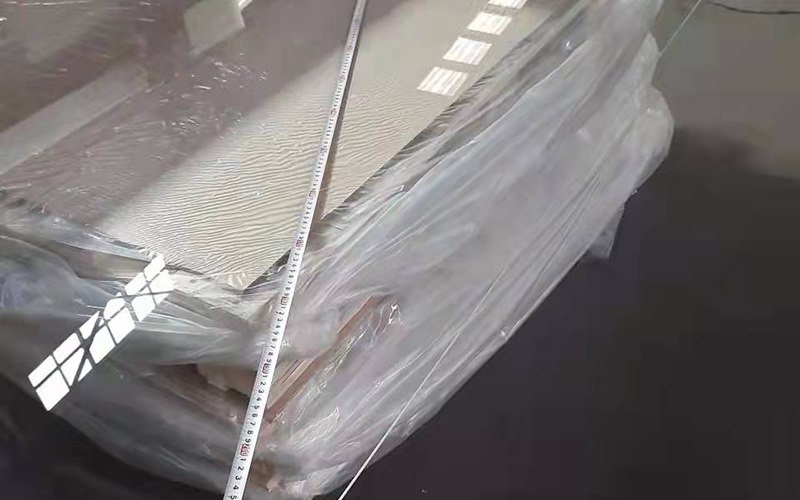

Inspection sizes 2000 960mm

Test transmittance rate
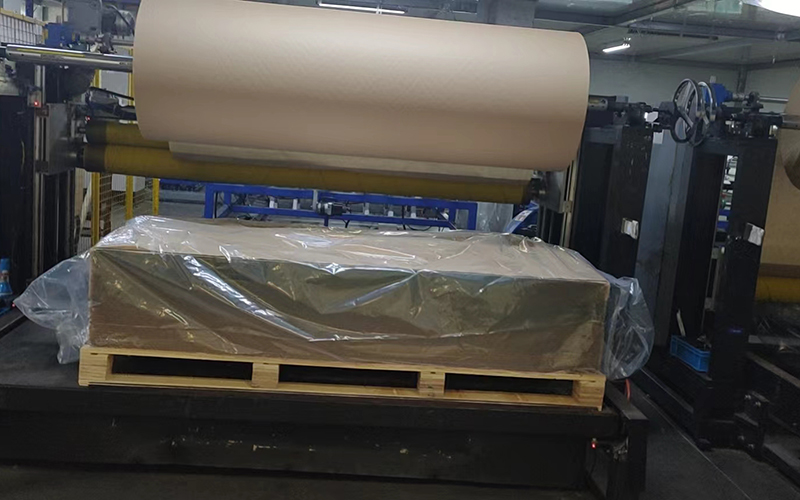

Solar glass packing process
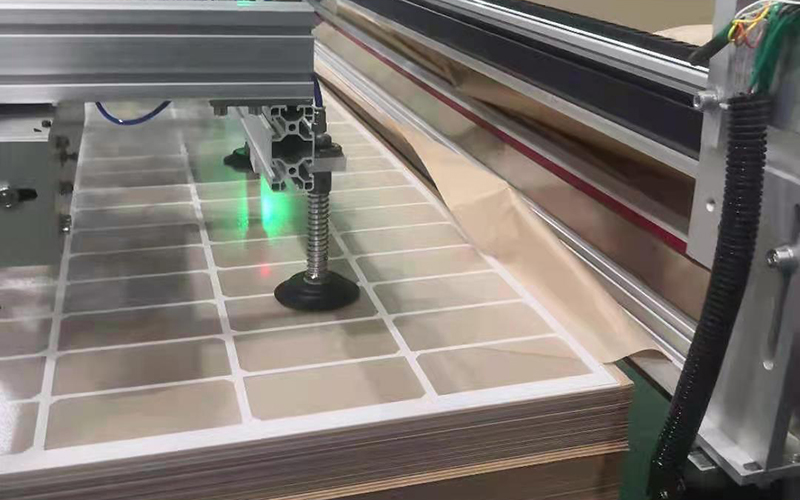

Silk print process

Raw glass warehouse

Processing

Processing

Pallets

![Borosil Renewable's solar glass furnace was modified to become more energy efficient and was also repaired at the cold end. [Image: Borosil Renewables]](https://www.glass-international.com/imager/news/216496/Borosil-Renewables-web_46527c80523046a5c0b3b8e30581599a.png)
How long to produce a batch of fused cast AZS blocks?
The production time for a batch of fused cast AZS blocks typically ranges from 3 to 8 weeks, depending on production scale, process complexity, and factory scheduling. Below is a breakdown of the timeline and key influencing factors:
I. Production Process & Time Estimates
1.Raw Material Preparation (1–2 weeks)
Procurement, testing, and proportioning of raw materials (Al₂O₃, ZrO₂, SiO₂, etc.).
Time may extend if preprocessing (e.g., crushing, purification) is required.
2.Melting (2–5 days)
High-temperature melting (≈1800°C–2000°C) in an electric arc furnace to form a homogeneous melt.
Duration depends on furnace capacity and process type (continuous vs. batch furnace).
3.Casting & Molding (1–3 days)
Pouring the molten material into custom molds for solidification.
Complex shapes or large-sized bricks require longer demolding times.
4.Annealing Treatment (5–10 days)
Slow cooling in annealing furnaces (≈10°C–30°C per day) to eliminate internal stress and prevent cracking.
This is the most time-critical phase, directly impacting product quality.
5.Machining & Post-Processing (3–7 days)
Cutting, grinding, drilling, etc., to meet dimensional accuracy.
Surface treatments (e.g., anti-oxidation coatings).
6.Quality Inspection & Packaging (2–5 days)
Testing density, composition, high-temperature resistance, etc.; reworking defects.
Packaging and logistics arrangements.
II. Key Factors Affecting Production Time
Order Size
Small batches (e.g., a few tons) may take 3–4 weeks, while large orders (tens of tons) may extend to 6–8 weeks.
Customization Requirements
Special shapes, sizes, or compositions (e.g., 33%/41% ZrO₂ content) require additional mold design and process adjustments.
Factory Scheduling & Equipment
Availability of electric arc furnaces and annealing furnaces; potential production queue delays.
Quality Control Rigor
High-precision testing or repeated annealing may extend timelines.
III. Options to Shorten the Cycle
Expedited Production: Prioritized scheduling or shift extensions (may incur higher costs).
Pre-prepared Materials: Stockpiling raw materials and molds can reduce timelines by 1–2 weeks.
Simplified Processes: Standard products are faster than custom designs but may compromise performance.
IV. Recommendations
Clarify technical specifications, delivery timelines, and quality standards with the manufacturer in a detailed contract.
Plan ahead, allowing at least 1–2 months (including logistics and contingency buffers).
Prioritize manufacturers with proven expertise to ensure process stability.
For precise timelines, contact suppliers directly and provide order specifics (e.g., brick type, quantity, ZrO₂ content) to obtain a detailed production schedule.
ادامه مطلب
Revolutionize Your Heating with Our Silicon Carbide Heating Elements! 🌟 Ultra-high temperature resistance, rapid heating, and long lifespan. Ideal for industrial furnaces, kilns & more. Precision-engineered for efficiency & durability. Trusted by global experts. Upgrade now! 💪
hashtag#Industrialheatingelementssupplier
hashtag#Electricfurnaceheatingsolutions
hashtag#Siliconcarbideheatingelements
hashtag#SiliconCarbideElectricHeater
hashtag#Siliconcarbideheatingelementmanufacturer
hashtag#Siliconcarbideheatingelementexporter
Activate to view larger image,
ادامه مطلب
Looking for High-Quality PVB Film?
We specialize in premium-grade PVB film for laminated safety glass, offering excellent optical clarity, adhesion, and durability. Ideal for automotive and architectural applications.
Interested in samples or specs? Let’s connect!
hashtag#PVBfilm hashtag#PVBManufacturer hashtag#SafetyGlass hashtag#ArchitecturalPVB hashtag#ColorPVB hashtag#AutomotivePVB hashtag#ArchitecturalGlass hashtag#AutomotiveGlass hashtag#ConstructionMaterials hashtag#GlassIndustry hashtag#LaminatedGlass
Activate to view larger image,
ادامه مطلب
آغاز بهکار زون نخست نیروگاه ۶۰۰ مگاواتی آفتاب شرق به كارفرمايي فولاد مباركه و با مشارکت شرکت گروه مپنا و مهندسين مشاور موننكوايران
زون نخست نیروگاه خورشیدی ۶۰۰ مگاواتی آفتاب شرق با ظرفیت ۱۲۰ مگاوات، به کارفرمایی شرکت فولاد مبارکه و با اجرای شرکت توسعه انرژیهای تجدیدپذیر مپنا (توسعه ۳) از گروه مپنا، در تاریخ ۱۵ اردیبهشت ۱۴۰۴ با موفقیت کامل به شبکه سراسری برق کشور متصل و سنکرون گردید. در این زون، ۱۲۰ مگاوات پنل خورشیدی با سازه ترکدار، ۱۸ اینورتر قدرتمند ۶.۲۵ مگاواتی، و اتصال به شبکه از طریق پست 63/33 کیلوولت پیادهسازی شده است.
شرکت مهندسین مشاور موننكوايران مسئولیت کامل طراحی مهندسی نیروگاه فتوولتائیک، طراحی و مهندسی پستهای برق و خطوط ارتباطی، و خدمات مهندسی خرید این پروژه بزرگ و ملی را برعهده داشته است. این پروژه با وسعتی بالغ بر ۱۲۰۰ هکتار، شامل ۹۰۹۱۵۰ پنل خورشیدی Bifacial و ۹۰ اینورتر پیشرفته بوده و در پنج زون ۱۲۰ مگاواتی طراحی شده است. اتصال به شبکه از طریق دو پست 63 و 400 کیلوولت انجام میگیرد که کلیه طراحیهای فنی آن توسط شرکت موننكوايران انجام شده است.
یک سوال پرتکرار: چرا در بیابانهای جهان نیروگاههای خورشیدی عظیم نمیسازیم؟
☀️ بیابانها پر از آفتاب، ولی خالی از نیروگاه!
بیابانهای جهان مانند صحرا، آتاکاما یا دشت لوت، پتانسیل عظیمی برای تولید انرژی خورشیدی دارند. پس چرا شاهد ساخت نیروگاههای چند هزار مگاواتی در این مناطق نیستیم؟ پاسخ این سؤال، ترکیبی از چالشهای فنی، اقتصادی و شبکهای است.
🔍 چالشهای کلیدی:
✅ ۱. تولید متناوب و نیاز به ذخیرهسازی:
نیروگاههای خورشیدی فقط در روز برق تولید میکنند، درحالی که شبکههای برق به تأمین ۲۴ ساعته نیاز دارند. راهحل، استفاده از باتریهای عظیم یا سیستمهای ذخیرهساز است که هنوز گران و کمظرفیت هستند. البته در نیروگاه های متمرکز کننده خورشیدی میتوان انرژی حرارتی را ذخیره کرد ولی فعلا این روش تولید انرژی مشکلاتی(مخصوصا اقتصادی) دارد.
✅ ۲. محدودیتهای انتقال انرژی:
انتقال برق از دل بیابان به شهرهای دور، نیاز به خطوط فشارقوی جدید دارد که هزینه ساخت و تلفات انرژی آنها بسیار بالاست. آیا شبکههای فعلی توان تحمل این بار را دارند؟
✅ ۳. چالشهای پایداری شبکه (دینامیک سیستم):
افزایش ناگهانی تزریق برق خورشیدی به شبکه میتواند پایداری فرکانس و ولتاژ را به خطر بیندازد. اتفاق اخیر در اسپانیا نمونه بارز این چالش بود. در یک روز ابری، کاهش ناگهانی تولید خورشیدی باعث نوسانات شدید در شبکه شد و اپراتورها را مجبور به استفاده سریع از نیروگاههای پشتیبان کرد. این رویداد نشان میدهد حتی کشورهای پیشرفته در حوزه انرژی تجدیدپذیر هم با چالش مدیریت شبکه در شرایط متغیر دست و پنجه نرم میکنند.
https://lnkd.in/ePGM5JR3
✅ ۴. مسائل اقتصادی و ریسک سرمایهگذاری:
ساخت یک نیروگاه چند هزار مگاواتی به جای چند نیروگاه کوچکتر، ریسک عملیاتی و مالی بالاتری دارد. همچنین، نگهداری تجهیزات در محیطهای کویری با گردوغبار و دمای بالا، چالشهای خاص خود را ایجاد میکند ضمن اینکه دمای بالا موجب کاهش توان تولیدی پانل های فتوولتائیک نیز می شود.
✅ ۵. ملاحظات محیطزیستی:
بیابانها فقط "زمینهای خالی" نیستند! بسیاری از این مناطق حیاتوحش منحصربهفرد دارند یا جزو مناطق حفاظتشده هستند. نصب پنلهای گسترده میتواند اکوسیستم را تحت تأثیر قرار دهد.
🌍 آیا این چالشها غیرقابلحل هستند؟
خیر! پروژههایی مانند:
· دیوار خورشیدی بزرگ چین (هدف: ۱۰۰ گیگاوات تا ۲۰۳۰)
https://lnkd.in/erQsY7iP
· پروژه نور مراکش (نیروگاه خورشیدی متمرکز + ذخیرهسازی حرارتی)
https://lnkd.in/eUAw-qnY
· طرح Xlinks مراکش-انگلیس (انتقال برق از صحرا به اروپا با کابل زیردریایی)
https://xlinks.co/
نشان میدهند که با فناوریهای جدید و سرمایهگذاری بلندمدت، میتوان از این پتانسیل استفاده کرد.
hashtag#انرژی_خورشیدی hashtag#نیروگاه_خورشیدی
hashtag#solar hashtag#solarenergy hashtag#solarpower
شیشه سولار چیست؟
دیدگاه خود را بنویسید / راهنمای خرید شیشه
در خودروهای مدرن امروزی شیشههای جلو و سقف به گونهای طراحی شده است، که احساس بازتر و جادارتر بودن فضای داخل خودرو را به سرنشینان القا میکند. با افزایش اندازه سایز شیشهها، نور خورشید بیشتر وارد فضای داخلی ماشین میشود. سازندگان خودرو برای اینکه نور خورشید کمتر وارد ماشین شود از شیشهسولار استفاده میکنند.
همانطور که بسیاری از افراد تجربه کردهاند، هنگامی که نور خورشید وارد وسیله نقلیه میشود، دمای داخل خودرو افزایش مییابد و شما گرما را روی پوست خود احساس میکنید. همچنین اشعه ماوراء بنفش نور خورشید میتواند از شیشههای شفاف جلو و دربها به داخل ماشین نفوذ کند. این اشعه برای سرنشینان و اجزاء داخل خودرو مضر است.
برای کاهش تاثیر نور خورشید در داخل ماشین، سازندگان شیشه خودرو راه حلهایی پیدا کردند. یکی از این راه حلها، تولید شیشه سولار است. شیشه سولار از دو لایه شیشه و یک لایه میانی تشکیل شده است. وجود این چند لایه، سبب مستحکم شدن شیشه خودرو میشود و می تواند در حل این مشکلات کمک کننده باشد.در ادامه به ویژگیهای شیشه و مزایای آن در خودروها می پردازیم. با ما همراه باشید.
اثرات نور خورشید بر بدن انسان
قبل از اینکه به ویژگیهای شیشه سولار (Solar Glass) بپردازیم این سوال پیش میآید که چرا شیشههای خودرو را باید سولار کرد؟مگر نور خورشید برای همه موجودات کره زمین برای ادامه حیات مفید و ضروری نیست؟
در پاسخ باید گفت: بله نور خورشید تاثیرات مثبتی بر بدن انسان دارد. به عنوان مثال نور خورشید باعث میشود ویتامین D که یکی از عوامل بازسازی استخوان در بدن است، بهتر جذب بدن شود. اما دقت داشته باشید که به مدت طولانی در معرض آفتاب قرار گرفتن بسیار خطرناک است و باعث بروز مشکلات زیر میشود:
۱- آفتاب سوختگی
۲- ایجاد بیماری هایی مثل لوپوس و کهیر
۳- ایجاد لکهای پوستی
۴- بیماریهای چشمی (آب مروارید و….)
۵-سرطان پوست
تمامی این بیماریها بخاطر اشعههای مضر نور خورشید است. نور خورشید شامل نور مرئی ، اشعه مادون قرمز و اشعه ماورا بنفش است. اشعه مادون قرمز مانند یک لامپ حرارتی است و باعث گرم شدن محیط میشود. اشعه ماوراء بنفش برای بدن مضر است و میتواند باعث بیماریهای پوستی شود. در نور خورشید دو نوع اشعه ماوراء بنفش(UV) وجود دارد : اشعه (UVA) و (UVB)
اشعه(UVA) قدرت نفوذ کمتری در بدن دارد و باعث چین و چروک پوست میشود. اما اشعه (UVB) قدرت نفوذ بیشتری دارد و در عمق بیشتری از پوست نفوذ می کند و قدرت تخریب بافت پوست را دارد و همین امر باعث مشکلات بیماریهای پوستی و در نهایت سرطان پوست میشود.
به همین دلیل در زمانهایی که به مدت طولانی در معرض نور خورشید قرار میگیرد، باید کاری کنید اثرات مضر نور خورشید را به حداقل برسانید.
استفاده از شیشه های سولار (Solar Glass)یکی از راهکارهای کاهش تاثیر مضر نور خورشید است.

شیشه سولار (Solar Glass)چیست؟
اکثر شیشههای شفاف و معمولی خودرو از شیشههای دو لایه ساخته شدهاند که از دو لایه شیشه با یک لایه پلاستیکی (pvb) به هم وکیوم شدهاند. اما شیشههای سولار خودرو، از دو لایه شیشه با یک لایه جذب کننده حرارت (لایه میانی) تشکیل شدهاست.
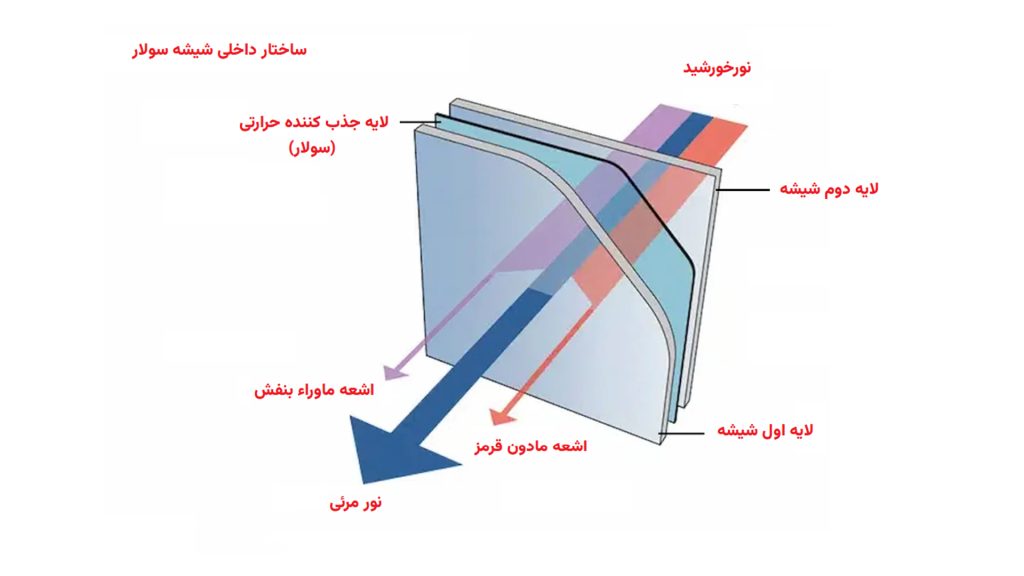
هنگامی که نور خورشید به شیشه سولار برخورد می کند، لایه جذب کننده حرارت از انتقال گرمای زیاد به داخل خودرو (اشعه مادون قرمز) جلوگیری میکند. خبر خوب این که شیشههای سولار، اشعههای فرابنفش (UV) خورشید را به دلیل وجود لایه میانی هم مسدود میکند.
ویژگیهای شیشه سولار(Solar Glass Property)
۱- شیشههای سولار اتومبیلها، افراد را از آسیبهای چشمی، برنزه شدن، آفتاب سوختگی و سرطان پوست که ممکن است در اثر اشعه UV مستقیم ایجاد شود، محافظت میکند.
۲- در دمای بالای تابستان، کابین وسیله نقلیه در روز تبدیل به یک کوره گرم میشود و موجب آزار سرنشینان و راننده میشود. در این زمان شیشه سولار نقش حیاتی ایفا میکند زیرا بیشتر پرتوهای مادون قرمز خورشید را جذب می کند و در نتیجه دمای داخل کابین کاهش مییابد و راننده و سرنشینان از سواری راحت خود لذت میبرند.علاوه بر این، گرما به اجزای داخل کابین خودرو نیز آسیب میرساند و باعث فرسوده شدن زود هنگام آنها میشود. شیشههای سولار در افزایش طول عمر و دوام آنها تاثیر به سزایی دارد و در چنین حالتی استفاده از شیشه سولار، رانندگان را از تعمیرات گران قیمت باز میدارد.
۳-شیشههای سولار به ماشین زیبایی خاصی میدهد. از آنجایی که ظاهر خودرو برای افراد زیادی به خصوص جوانان اهمیت بالایی دارد، استفاده از این شیشهها زیبایی خودرو را دوچندان میکند و ظاهری شیکتر و اسپرتتر به آن میدهد.
۴- وضوح و کیفیت دید و همچنین عدم تغییر رنگ مناظر و تصاویر یکی دیگر از مزیتهای این شیشهها است که شما با استفاده از این شیشهها، هیچ گونه تغییر رنگ یا تاری دید حتی در آب و هوای ابری یا در شب نخواهید داشت.
۵- شیشههای سولار مادام العمر هستند و نیازی نیست شما هر چند سال برای نصب مجدد آنها هزینه کنید.

تفاوت شیشه سولار با برچسب دودی
در این قسمت قصد داریم شما را با تفاوت های شیشه های سولار و دودی (شیشههای برچسبدار) بیشتر آشنا کنیم.
- شیشههای برچسبدار که منظور همان برچسبهای دودی هستند که روی شیشههای خودرو نصب میشوند معمولا رنگ غیرطبیعی دارند و بر رنگ تصاویر و مناظر بیرون و همچنین بر وضوح و شفافیت دید راننده و سرنشینان تاثیر منفی دارند. در حالی که شیشههای سولار رنگ طبیعی، وضوح و شفافیت بسیار بالایی دارند و دید راننده در حین رانندگی بسیار خوب است. مناظر بیرون در هوای ابری شفاف دیده میشود و باعث تغییر رنگ تصاویر و مناظر بیرون نمیشوند.
- رانندگی در شب با شیشههای برچسبدار به دلیل تیرگی ثابتی که دارد، باعث اختلال در دید راننده از آینههای وسط و پهلو میشود و احتمال تصادفات مرگبار و جبرانناپذیر را بالا میبرد. در صورتی که در شیشههای سولار به دلیل متغیر بودن رنگ دودی شیشه، در شب کمترین مقدار دودی را دارد و دید بهتری راننده در حین رانندگی دارد.
- تفاوت دیگر در کیفیت این دو شیشه است، شیشه های دودی به مرور کیفیت خود را از دست میدهند و همچنین احتمال اینکه خط و خش روی آنها ایجاد شود وجود دارد. مثلا در هنگام تمیز کردن، تماس هرگونه جسم زبر با این برچسبها ممکن است به آنها خراش وارد کند و شما مجبور هستید هر چندسال یک بار هزینه کنید و برچسبها را تعویض کنید. در حالی که شیشه های سولار کیفیت بسیار بالایی دارند و خط و خش نمی تواند به آنها آسیب برساند. زیرا لایه دودی مابین دو لایه شیشه قرار میگیرد و تا مدت ها، شما میتوانید از این شیشهها استفاده کنید.
- شیشههای دودی برچسبی بسته به درجهبندی میزان دودی بودن، می توانند مجوز تردد داشته باشند، مثلا در کشور ما طبق قوانین راهنمایی رانندگی خودروهایی که دارای شیشههای دودی با درصد ۳۵ تا ۴۰ تیرگی، مجوز تردد دارند. شیشههایی که درصد تیرگی آنها از این مقدار بالاتر باشد جریمه خواهند شد و در برخی موارد احتمال توقیف خودرو نیز وجود دارد. در حالی که شیشههای سولار طبق مطابق با استاندارد های کمپانی سازنده خودرو است و هولوگرام روی شیشه، تایید کننده این مطلب است. همچنین با قوانین پلیس راهور همخوانی دارد.
- مورد دیگری که در تفاوت بین این دو شیشه باید به آن اشاره کنیم، این است که شیشههای سولار uv400 هستند. به همین دلیل اشعههای مضر فرابنفش را مسدود میکنند و از آسیب رسیدن به پوست راننده و سرنشینان جلوگیری میکنند. همچنین همین مزیت باعث میشود کیفیت اجزای کابین (داشبورد، صندلی و….) در دراز مدت حفظ شود و به مرور فرسوده و خراب نشوند. همچنین حذف اشعه UV در معتدل شدن هوای داخل خودرو تاثیر مثبت دارد و باعث بهبود عملکرد کولر و تهویه هوا می شوند. چرا که این شیشهها مانع تابش مستقیم نور خورشید به داخل خودرو میشوند و در نتیجه گرمای داخل خودرو کم میشود. در صورتی که شیشههای دودی برچسب دار، این خاصیت را ندارند.
با توجه به مواردی که در تفاوت بین این دو مدل شیشه گفته شد، دودی کردن شیشهها با برچسبهای دودی منطقی به نظر نمیرسد.

نکاتی که در مورد شیشه های سولار باید بدانید:
- ضخامت این شیشهها مشابه شیشههای فابریک سازنده خودرو است و تفاوتی با آنها ندارد.
- درصد تیرگی این شیشهها به شدت نور بستگی دارد یعنی با افزایش نور، تیرگی بیشتر و با کاهش نور، تیرگی کمتر میشود.
- تیرگی این شیشهها طبق استاندارد پلیس راهور است و هولوگرام سازنده خودرو روی آنها حک شده است.
- شیشههای سولار کاملا ضد خط و خش هستند و افت رنگ و وضوح دید ندارند.
- شیشه سولار یک آپشن بسیار خاص برای خودرو میباشد خصوصاً در هنگام فروش خودرو.
- شیشههای سولار معمولا برای تمام قسمتهای شیشهخور خودرو تولید میشود. بدین معنا که میتوانید از شیشههای سولار برای شیشههای جلو، عقب ، شیشه های درب اتومبیل و حتی شیشههای سقف استفاده کنید.
جمع بندی
در این مقاله سعی کردیم شما را با شیشه سولار (Solar Glass)و تفاوتهای آن با شیشههای برچسبدار بیشتر آشنا کنیم. همچنین به مزایای فراوان و جذاب این شیشهها نیز پرداختیم تا شما دید و آگاهی بهتری نسبت به شیشههای سولار به دست آورید تا بتوانید بهترین انتخاب برای خودروی خود و تجربه لذت بخش از یک رانندگی را داشته باشید.
𝗖𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗮 𝗚𝗹𝗮𝘀𝘀 𝟮𝟬𝟮𝟱 | 𝗪𝗲’𝗿𝗲 𝗘𝘅𝗵𝗶𝗯𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴! 🔹
📅 Mark your calendar and come meet us in person!
Whether you're looking for energy-efficient insulation, durable refractories, or tailored solutions for glass furnace lining, we’re ready to share how our materials can help optimize performance and reduce costs.
💬 Let’s talk about your upcoming projects
👀 Explore our latest products and innovations
🤝 Build valuable connections
Contact: Ali
📱 WhatsApp / WeChat: 00989123812602
We look forward to seeing you in Beijing!
hashtag#ChinaGlass2025 hashtag#GlassIndustry hashtag#RefractorySolutions hashtag#InsulationMaterials hashtag#FurnaceLining hashtag#FirebirdMaterials hashtag#GlassFurnace hashtag#Exhibition
.: Weblog Themes By Pichak :.










